Data Deposition and Annotation
Deposition Statistics
From July 1-September 30, 2012, 2583 experimentally-determined structures were deposited to the PDB archive, and then processed and annotated by wwPDB teams.
Of the structures deposited in 2012 so far, 81% were deposited with a release status of hold until publication; 15% were released as soon as annotation of the entry was complete; and 4% were held until a particular date. 93% of these entries were determined by X-ray crystallographic methods; 6% were determined by NMR methods.
During the same time period, 2167 structures were released and made publicly available in the PDB.
Prepare Data for Deposition with pdb_extract and SF-Tool
Tools are available to help prepare data files for deposition with ADIT. Using these resources can help minimize errors, validate data, and save time during the deposition process.
pdb_extract extracts key details from the output files produced by many X-ray crystallographic and NMR applications. The program merges these data into mmCIF data files that can be used with ADIT for validation and deposition.
 pdb_extract features include support for:
pdb_extract features include support for:
- Data from hybrid method experiments
- NCS and TLS ranges in BUSTER and REFMAC
- Improved mtz-to-mmCIF conversion
- Quality assessment of X-ray data
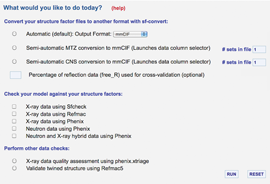
SF-Tool is a streamlined, web-based tool for validating X-ray, neutron, and hybrid experimental data. Visit sf-tool.rcsb.org to:
- Validate model coordinates against structure factor data
- Easily convert structure factor files between different formats (mmCIF, MTZ, CNS/CNX, XPLOR, SHELX, TNT, HKL2000, SCALEPACK, D*Trek, SAINT, and more)
- Check for and validate twinned or detwinned data
wwPDB News:
Special Symposium on PDB: Basis for Life Science and Drug Development
A special PDB symposium will be held on Saturday, October 13, 2012 at Hearton Hall in Osaka, Japan. The meeting is free and open to the public.
Presentations will include:
- wwPDB and its Impacts on Science and Society, Haruki Nakamura, Osaka University
- Impact of the Protein Data Bank on Drug Discovery, Stephen Kevin Burley, University of California at San Diego
- Molecular Nanomachines in Living Organisms-Exquisite Structural Design Far Beyond State-of-the-Art Nanotechnology, Keiichi Namba, Osaka University
For more information, see wwpdb.org.
Science as an open enterprise
The wwPDB's management of the PDB archive was highlighted as a major international data initiative with well-defined protocols for the selection and incorporation of new data and access to them in a report from The Royal Society on openness in scientific data. The full report, entitled Science as an open enterprise, is online at royalsociety.org.
- G. N. Murshudov, A. A. Vagin, E. J. Dodson. (1997) Refinement of macromolecular structures by the maximum-likelihood method. Acta Crystallogr. D53: 240-255.
- P. D. Adams, R. W. Grosse-Kunstleve, L.-W. Hung, T. R. Ioerger, A. j. McCoy, N. W. Moriarty, R. J. Read, J. C. Sacchettini, N. K. Sauter, T. C. Terwilliger. (2002) PHENIX: building new software for automated crystallographic structure determination. Acta Crystallographica D58: 1948-1954.
- A. A. Vaguine, J. Richelle, S. J. Wodak. (1999) SFCHECK: a unified set of procedures for evaluating the quality of macromolecular structure-factor data and their agreement with the atomic model. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 55: 191-205.